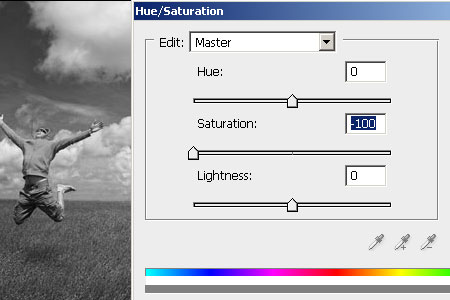
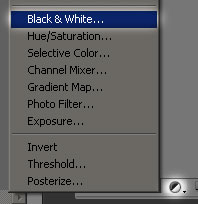
Step 1: Duplicate The Background Layer
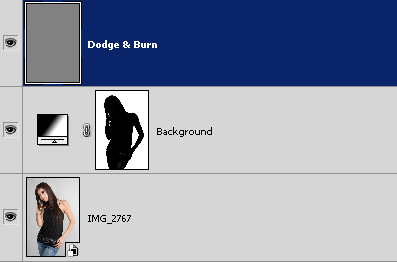
The first thing we need to do for this effect is duplicate our Background layer. With our image open in Photoshop, we can see in the Layers palette that we currently have just one layer, the Background layer, which contains our original image:

To quickly duplicate the layer, use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+J (Win) / Command+J (Mac). Photoshop creates a copy of the Background layer for us, names it "Layer 1", and places it above our Background layer in the Layers palette:

Step 2: Add A New Blank Layer Between The Two Layers
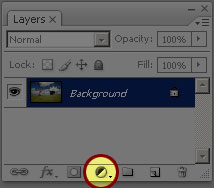
Next, we need to add a new blank layer between our Background layer and the copy of it that we just created. Currently the copy is selected in the Layers palette (we can tell the layer is selected because it's highlighted in blue). Normally when we add a new layer, Photoshop places the new layer above the layer that's currently selected, but we want our new layer below "Layer 1", not above it. To tell Photoshop to place the new layer below "Layer 1", hold down your Ctrl (Win) / Command (Mac) key and then click on the New Layer icon at the bottom of the Layers palette:
![]()
Photoshop adds a new blank layer named "Layer 2" between "Layer 1" and the original Background layer:

Step 3: Fill The New Layer With Black
We're going to use black as the background for our effect, so let's reset our Foreground and Background colors if needed by pressing D on your keyboard. This sets black as your Foreground color and white as your Background color, as we can see in the Foreground and Background color swatches near the bottom of the Tools palette:

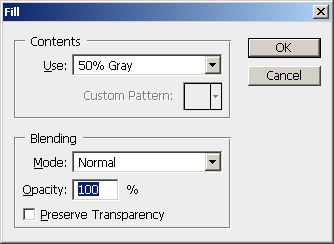
Now with black as our Foreground color and the new blank layer selected in the Layers palette, let's fill the new layer with black using the keyboard shortcut Alt+Backspace (Win) / Option+Delete (Mac). Nothing will appear to have happened to the image itself, and that's because "Layer 1", which contains a copy of our original image, is blocking "Layer 2" from view. But if we look at Layer 2's thumbnail in the Layers palette, we can see that we've filled the layer with black:

Step 4: Add A New Blank Layer
With "Layer 2" (the layer we just filled with black) selected, click once again on the New Layer icon at the bottom of the Layers palette:
![]()
Photoshop will add a new blank layer between the black-filled layer and the copy of the original image above it:

Step 5: Drag Out A Rectangular Selection As The Inside Of Your First Polaroid
Select the Rectangular Marquee Tool either from the Tools palette or by pressing M on your keyboard:

Then, with the Rectangular Marquee Tool selected, drag out a selection inside your image which will become the inside of the first polaroid (the part which contains the photo). I'm going to drag my selection around the baby's face. It doesn't really matter where you make this selection since you'll be able to move it anywhere you like later:

Step 6: Fill The Selection With Black
We need to fill the selection with black at this point. Technically, it doesn't matter which color we fill the selection with, but to keep things simple and since black is currently our Foreground color, let's use black. Make sure you have the new blank layer selected in the Layers palette, and then use the keyboard shortcut Alt+Backspace (Win) / Option+Delete (Mac) to fill the selection with the Foreground color, which is set to black. Again, nothing seems to have happened in the document, and that's because the image on "Layer 1" at the top is still blocking everything else from view, but if we look at the thumbnail for the blank layer in the Layers palette, we can see that the selected area has indeed been filled with black:

Step 7: Create A Clipping Mask From The Filled Selection
We're going to use the selection we just filled with black to create what's called a clipping mask for the layer above it. What this means is that the layer above it, "Layer 1" which contains the copy of our image, is going to be "clipped" by our filled selection on the layer below it. In other words, the only part of the image on "Layer 1" that will remain visible is the part directly above the section filled with black. The rest of the image will become hidden from view. To create our clipping mask, click on "Layer 1" to select it in the Layers palette. Then go up to the Layer menu at the top of the screen and select Create Clipping Mask. You can also use the keyboard shortcut Alt+Ctrl+G (Win) / Option+Command+G (Mac). Either way, Photoshop "clips" the image on "Layer 1", keeping only the area above the black-filled shape below it visible and hiding the rest of the image, revealing our black background on "Layer 2" in its place:

If we look in the Layers palette now, we can see that "Layer 1" is indented to the right with a small arrow pointing downward on the left. This indicates that the layer is being clipped by the layer below it:

Step 8: Add Another New Blank Layer Above "Layer 2"
We need to add another new layer, and we need it between the black-filled layer ("Layer 2") and the layer containing our filled selection ("Layer 3"). To do that, click on "Layer 2" to select it and then click once again on the New Layer icon at the bottom of the Layers palette:

Photoshop adds the new layer between "Layer 2" and "Layer 3" and names it, surprisingly enough, "Layer 4":

Step 9: Drag Out Another Rectangular Selection As The Border Of The Polaroid
With your Rectangular Marquee Tool still selected, drag out another rectangular selection, this time around the outside of the original selection, which will become the white border of the polaroid. Keep in mind that polaroid photos have some extra space at the bottom of the border, so add some extra space at the bottom of your selection:

Step 10: Fill The Selection With White
Since the border of a polaroid is usually white, let's fill our selection with white. Make sure that you have the new blank layer, "Layer 4", selected in the Layers palette. Then, since white is currently our Background color, let's use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Backspace (Win) / Command+Delete (Mac) to fill the selection with the Background color (white). Press Ctrl+D (Win) / Command+D (Mac) when you're done to deselect the selection. We now have our first polaroid in our image:

Step 11: Add A Drop Shadow Layer Style
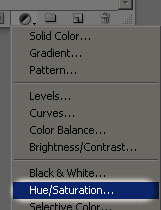
We have our first polaroid, and we're going to use it to easily create as many polaroids as we want. But before we do anything else, let's add a slight drop shadow to it. We won't be able to see the drop shadow just yet, since we're using a black background, but we will see it once we start piling polaroids on top of each other. To add our drop shadow, with "Layer 4" selected, click on the Layer Styles icon at the bottom of the Layers palette:
![]()
Select Drop Shadow from the list of layer styles:

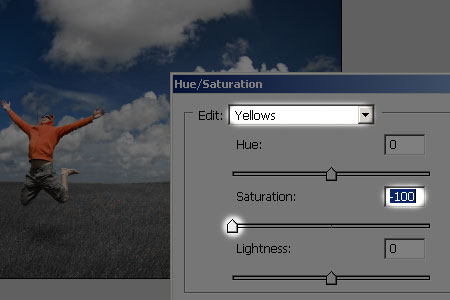
This brings up Photoshop's "Layer Style" dialog box set to the Drop Shadow options in the middle column. I'm going to set my shadow Angle to about 120° and then lower the Opacity value at the top all the way down to about 30% so my shadow isn't too intense:

Click OK to exit out of the Layer Style dialog box. As I said, we won't be able to see the drop shadow just yet thanks to our black background, but don't worry. We'll see it soon enough.
Step 12: Rotate The Polaroid
I'm going to rotate my polaroid to add a bit more interest to it. In order to do that, I need to select both layers in my Layers palette which make up my polaroid. I already have "Layer 4" selected, which makes up the outside of it, but I also need "Layer 3" selected, which makes up the inside, so with "Layer 4" selected, I'm going to hold down my Shift key and click on "Layer 3", which will select both layers at once (they'll both appear highlighted in blue):

Then with both layers selected, I'm going to bring up Photoshop's Free Transform handles around my polaroid using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+T (Win) / Command+T (Mac). To rotate it, all I need to do is drag my mouse cursor anywhere outside of the Free Transform handles. The mouse cursor will change to a "rotate" cursor with curved arrows on either end of it. As I drag my mouse, the polaroid will rotate:

You can also move the polaroid to a new location if you wish by clicking inside of it and dragging it around the screen with your mouse. I'm going to leave mine where it is for now and simply rotate it. As you drag, you'll notice that the border of the polaroid moves and rotates but the image inside of it does not, and that's because we're not moving the actual image. It remains fixed in place. The only thing we're moving is the polaroid itself, and this is what's going to allow us to create our final effect, as we'll see.
When you're happy with the location and angle of the polaroid , press Enter (Win) / Return (Mac) to apply the transformation.
Step 13: Group All Three Layers Which Make Up The Polaroid
We have our first polaroid created and rotated into place. Now we're going to use it to create as many polaroids as we want. Before we can do that though, we need to group all three layers which make up the polaroid , which are the top three layers in the Layers palette. "Layer 1" contains the image itself, "Layer 3" contains the inside of the polaroid , and "Layer 4" contains the outside of it. In order to group them, we need them all selected. We already have "Layer 3" and "Layer 4" selected, so once again hold down your Shift key and click on "Layer 1" to add it, so all three layers are selected and highlighted in blue:

Then, with all three layer selected, use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+G (Win) / Command+G (Mac) to group them. You'll see all three layers disappear from the Layers palette and be replaced by a layer named "Group 1", which contains a folder icon to indicate that it's a Layer Group. If you click on the right-pointing triangle to the left of the folder icon, the group will open and you'll see your three layers inside of it:

Step 14: Duplicate The Layer Group
We're going to use this Layer Group to create our second polaroid , and we're going to do that by duplicating the group. First, click once again on the triangle to the left of the folder in the Layers palette to close the group so your Layers palette doesn't get too cluttered. Then simply click on the group and drag it down onto the New Layer icon at the bottom of the Layers palette:

When you release your mouse button, you'll see the copy of the Layer Group appear above the original:

Step 15: Move And Rotate The Second Polaroid With The Free Transform Command
Just as we did with the original, we're going to move and rotate this second polaroid using Free Transform (I didn't actually move my first one, but you may have, so let's pretend I did as well). First, twirl open the newly created copy of our Layer Group by clicking on the triangle to the left of its folder icon. Just as before, you'll see all three layers inside of it which make up the polaroid . We need to select the bottom two layers which make up the inside and outside of it, so click on one, then hold down Shift and click on the other to select them both:

Then with both layers selected, press Ctrl+T (Win) / Command+T (Mac) to bring up the Free Transform handles around the polaroid . At the moment, it looks like there's only the one polaroid in the image, and that's because both of them are directly on top of each other. Click inside the polaroid and drag it to move it to a new location, and you'll see that you do in fact have two. Drag this second one to wherever you like in your document, and then rotate it just as before, by moving your mouse anywhere outside of the Free Transform handles and dragging your mouse to rotate it left or right. You'll see that once again, we're only moving the polaroid itself. The image inside of it remains fixed in place, and now that we've added a second polaroid , we're displaying more of the full size image:

You'll also notice that with the second polaroid overlapping the original, we can now see the drop shadow, which gives the image a bit of depth. When you're happy with the location and angle of your second polaroid , press Enter (Win) / Return (Mac) to apply the transformation. We now have two polaroids completed:

Step 16: Add, Move And Rotate More Polaroids As Needed
At this point, we just repeat the exact same process over and over until we've added enough polaroids to reveal enough of the original image. First, drag the top-most Layer Group down onto the New Layer icon at the bottom of the Layers palette. This will create a copy of the last polaroid you made. Then twirl the new Layer Group open by clicking on the arrow to the left of its folder icon and select the two bottom layers which make up the inside and outside of the polaroid. Press Ctrl+T (Win) / Command+T (Mac) to bring up the Free Transform handles, click inside them and drag the image into a new location to reveal more of the overall image, then move your mouse outside of the handles and drag to rotate the new polaroid. Press Enter (Win) / Return (Mac) to accept the transformation, then repeat the process again until you've added enough polaroids that you're happy with the results. There's no "right or wrong" placement of the polaroids , so don't be afraid to play around with it, and you can always go back and move or rotate any of the polaroids at any time by selecting its Layer Group, twirling it open, selecting the two bottom layers, then using Free Transform to move and/or rotate it again.
I'm going to add, move and rotate more polaroids here with my image, and after creating about 16 polaroids, moving and rotating each with the Free Transform command, here is my final result:

And there we have it!